Introduction
Bushcraft skills provide essential tools for outdoor survival, and shelter-building ranks among the most critical. A well-designed bushcraft shelter not only protects you from elements but also enhances your overall outdoor experience. Understanding how to create an effective shelter can mean the difference between comfort and discomfort in the wilderness. In this article, we will guide you through the essential principles of bushcraft shelter design, ensuring you are well-prepared for your next outdoor adventure.
We will explore various types of shelters, construction techniques, and materials suited for different environments. Whether you hike in forests, deserts, or snowy terrains, this comprehensive guide will help you master the art of building a shelter. Get ready to delve into the world of bushcraft and learn how to create a cozy retreat that keeps you safe and comfortable in nature.
Understanding Bushcraft The Importance of Shelter in Survival Situations

Bushcraft involves using skills from nature for survival and self-sufficiency. Among these skills, shelter-building stands out as a crucial element. A strong shelter offers protection from harsh weather, predators, and insects. It serves as a place to rest, cook, and store gear. Learning how to construct effective shelters can mean the difference between comfort and discomfort during outdoor adventures.
When facing the elements, a sturdy shelter can keep you warm and dry. Secrets to successful shelter-building lie in selecting the right location and materials. Choose a flat, dry area away from dangers like falling branches or water runoff. Using local resources like branches, leaves, and dirt can create a structure that withstands wind and rain. Mastery of these techniques builds confidence and encourages exploration in the great outdoors.
Types of Bushcraft Shelters Smart Designs for Outdoor Comfort
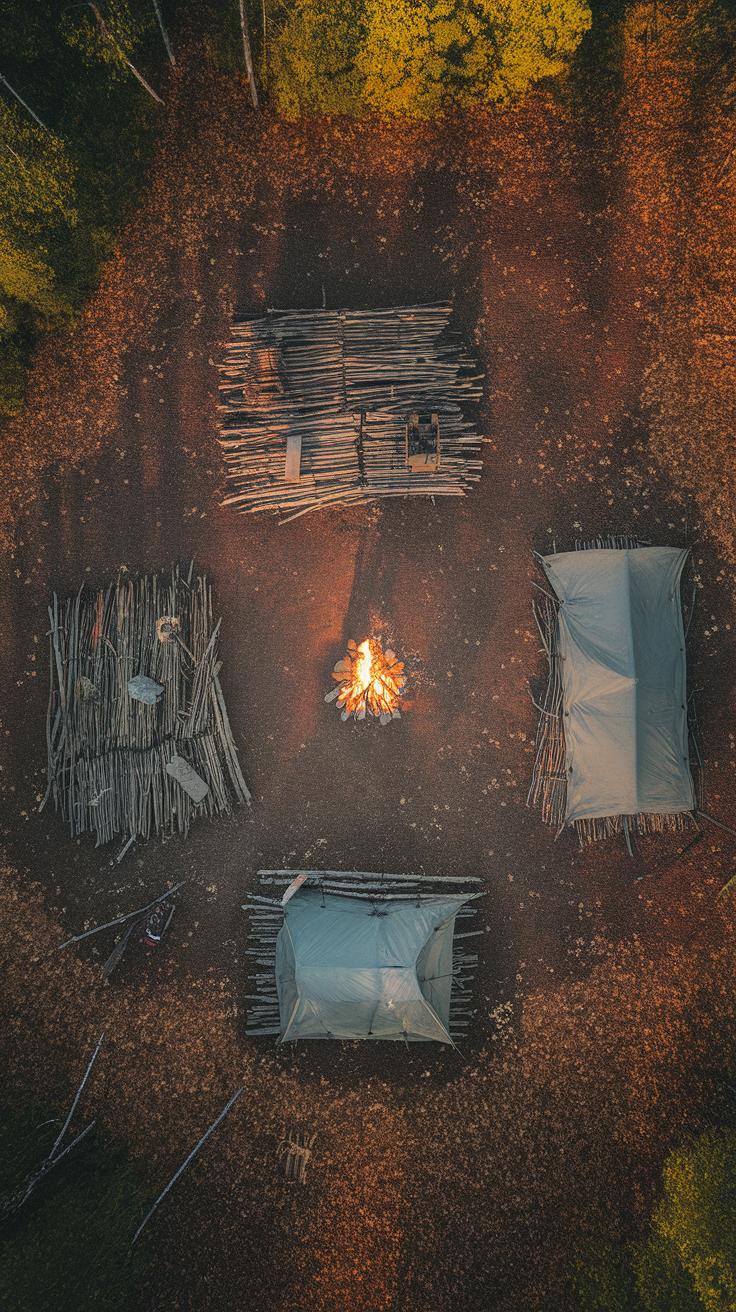

Common Bushcraft Shelter Types
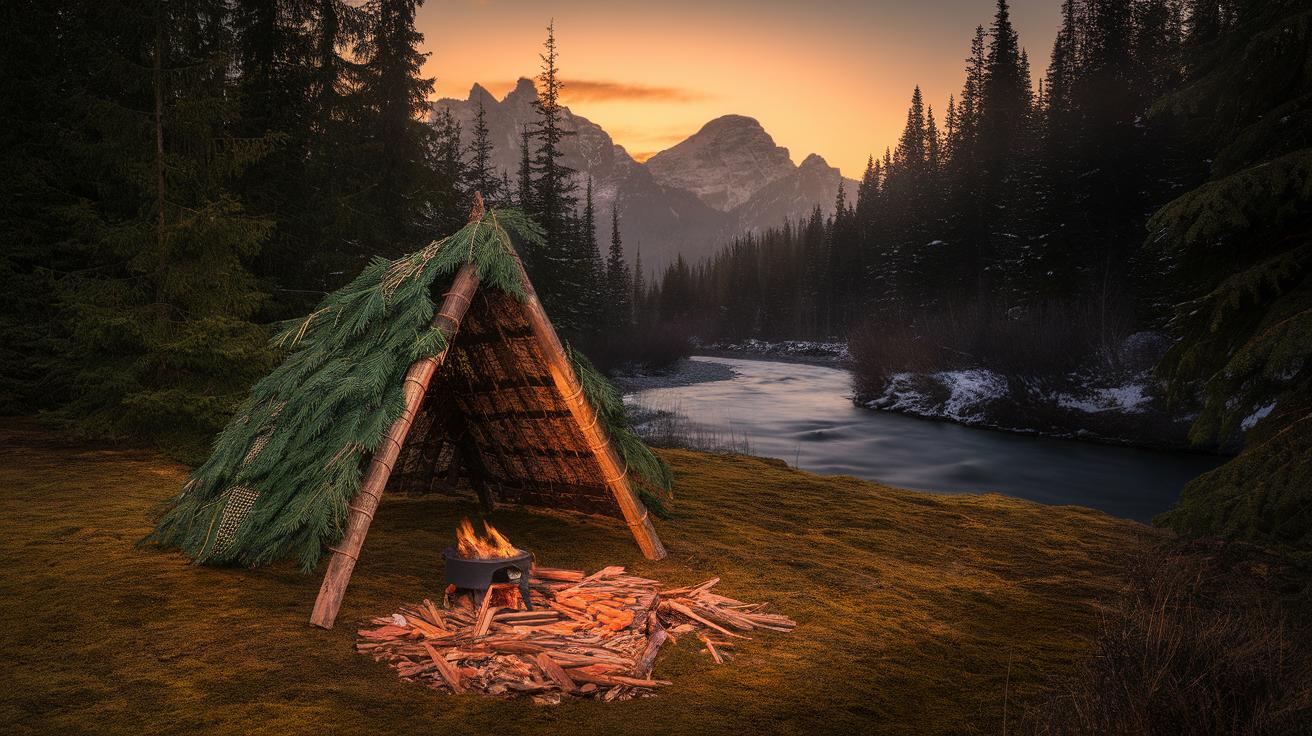
Bushcraft shelters come in various forms, each designed to meet different outdoor needs. One popular option is the lean-to. This simple structure uses branches and a tarp or foliage for cover. Lean-tos offer good protection from rain and wind, but they may not provide complete insulation against cold weather.
Another common shelter is the debris hut. This design uses natural materials like leaves and branches to create insulation. Debris huts excel in cold conditions, offering warmth, but they take longer to build and require more resources. Lastly, traditional tents remain a favorite due to their portability and ease of setup. However, tents often need ground space and don’t always blend with the natural environment, which can reduce camouflage.
Pros and Cons of Each Shelter
When selecting a shelter, consider the pros and cons. Lean-tos provide quick shelter but may lack warmth for cold nights. Debris huts trap heat effectively while using natural materials but need time to construct. Tents offer convenience and comfort, yet they might not suit all terrains or conditions. Understanding these shelter types helps you design smart bushcraft shelters for outdoor comfort, making your adventures more enjoyable.
Selecting the Right Location for Bushcraft Shelter

Finding Safety First
Choosing the right spot for your bushcraft shelter plays a huge role in your outdoor comfort. Start by looking for level ground where water won’t collect. Avoid building near dead trees, as they might fall during storms. Also, keep a safe distance from wildlife pathways to reduce encounters with animals. Look for natural barriers, like hills or dense bushes, which can shield you from wind and rain.
Assessing Available Resources
Next, examine the availability of materials. Look for fallen branches, leaves, and stones that can help you construct your shelter. Access to clean water nearby makes life easier, too. When planning, consider the direction of the sun; you might want some sunlight in the morning for warmth. Always think about the conveniences nearby, as that will make your camping experience more enjoyable.
Materials for Shelter Construction Selecting Natural and Synthetic Options for Comfort
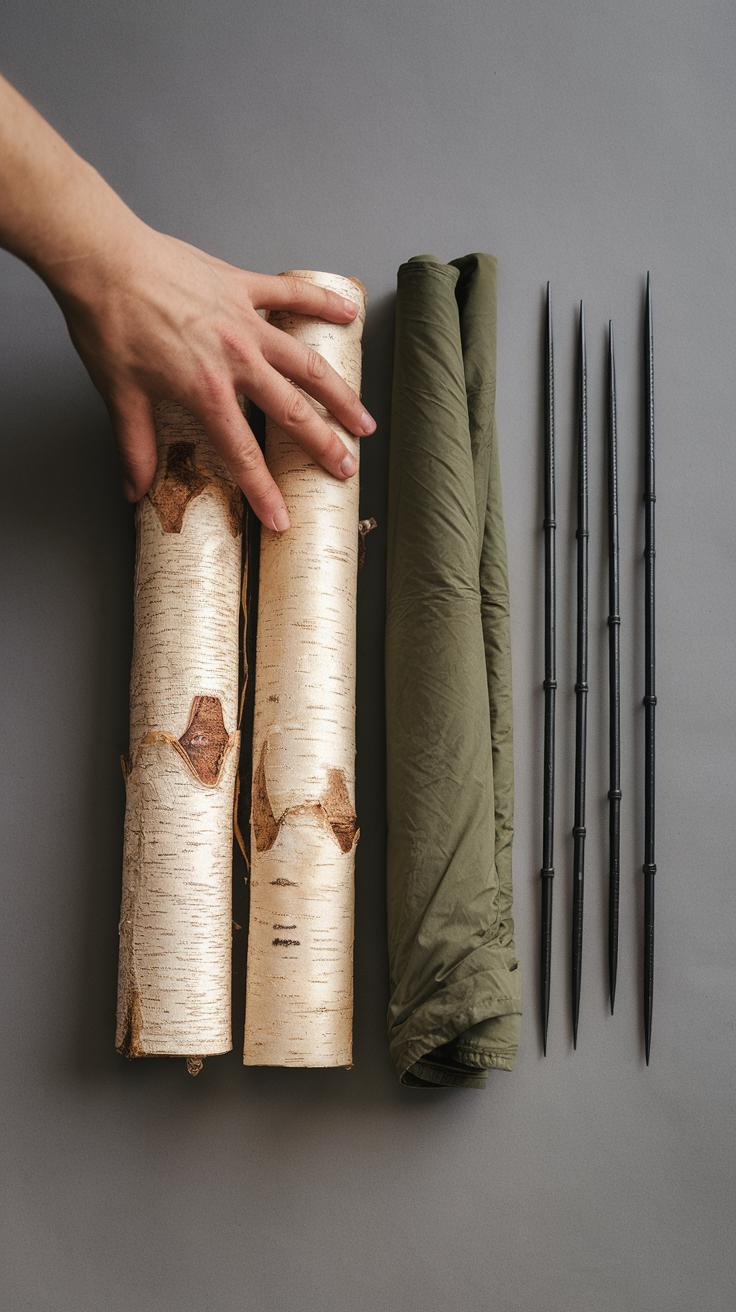

Natural Materials for Bushcraft Shelters
Using natural materials for shelter construction offers unique benefits. Woods like pine, cedar, and oak provide strong structural support due to their durability. Pine needles and leaves make excellent insulation, keeping shelters warm during cold nights. Grass, reeds, and bamboo serve well for thatch roofs, effectively repelling rain. Stone and mud can also help create strong walls that resist wind and keep pests out. Each natural material connects you to your environment, allowing you to blend in while benefiting from the resources around you.
Synthetic Materials for Enhanced Functionality
Synthetic materials also play a vital role in modern shelter building. Tarps and nylon fabric offer waterproof protection and can be lightweight for easy transport. Reflective space blankets provide warmth and reflect heat when tucked around a shelter. Ropes and cords made from synthetic fibers provide strength for securing structures while resisting wear. These materials combine practicality with convenience, making your outdoor experience comfortable and safe.
Basic Shelter Building Techniques
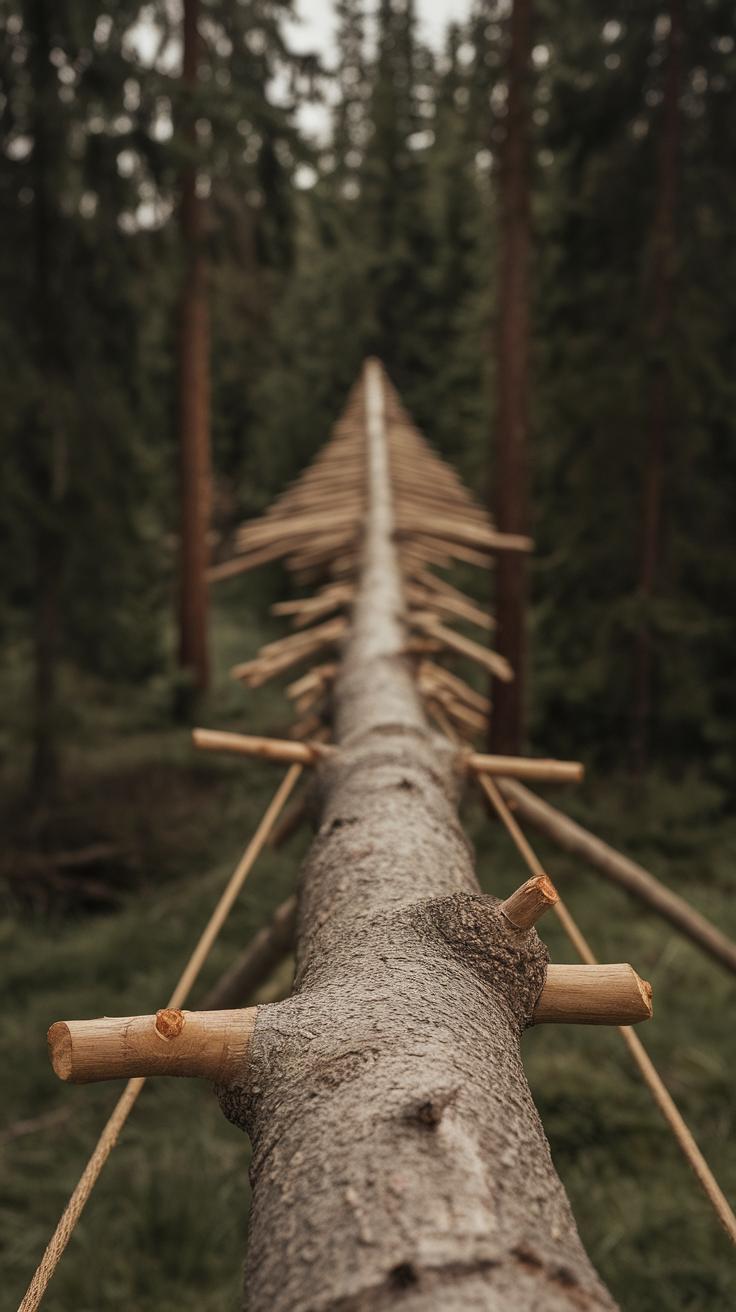

Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Shelter
Constructing a bushcraft shelter involves planning and following a methodical approach. Start by selecting a suitable location. Look for flat ground, away from hazards like falling branches or flooding. Next, gather materials such as branches, leaves, and stones. Use sturdy branches for the frame; you can create a simple A-frame by leaning branches against a central support. Secure the framework using smaller branches or vines to keep it stable.
Once the frame is ready, cover it with foliage and bark to insulate against wind and rain. Place thicker materials at the bottom to block drafts, and layer lighter materials on top for added protection. After building, check for gaps that could let water or wind in, and fill them in with extra leaves or moss. This process creates a warm, dry space for your bushcraft adventures.
Improvisation in Shelter Building
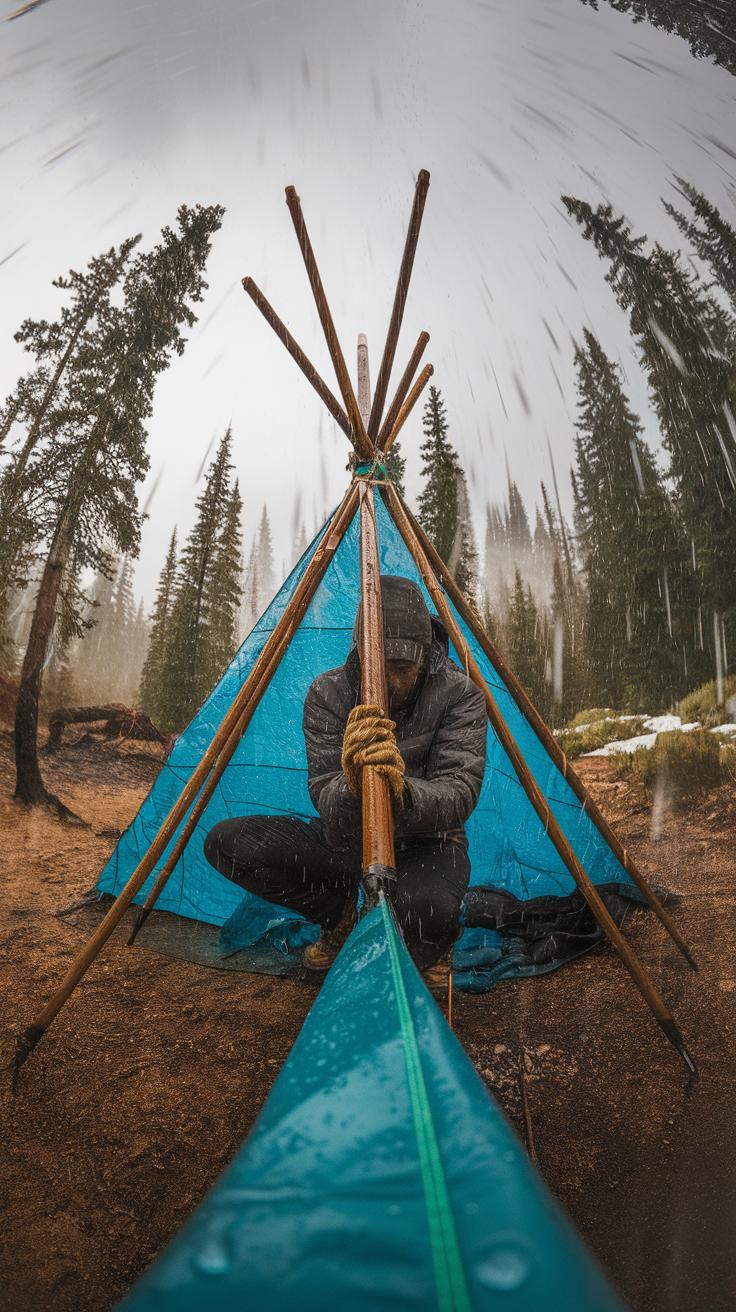

The Role of Creativity
Improvisation skills prove vital when building a bushcraft shelter. Often, the environment offers materials that you can repurpose into useful components for your shelter. For instance, fallen branches, leaves, and moss can create a sturdy framework and insulation. Observing your surroundings and thinking creatively allows you to adapt your shelter to various conditions, enhancing its stability and comfort.
Emphasizing Flexibility
Flexibility plays a big role in successful shelter construction. Different environments present unique challenges and opportunities. When you assess your surroundings, you develop the ability to modify your plans based on the available resources. For example, if you can’t find straight branches for the frame, bending flexible saplings can work just as well. This adaptability empowers you to create a safe, effective shelter no matter the location.
Maintaining Comfort in Your Shelter Techniques for Outdoor Comfort
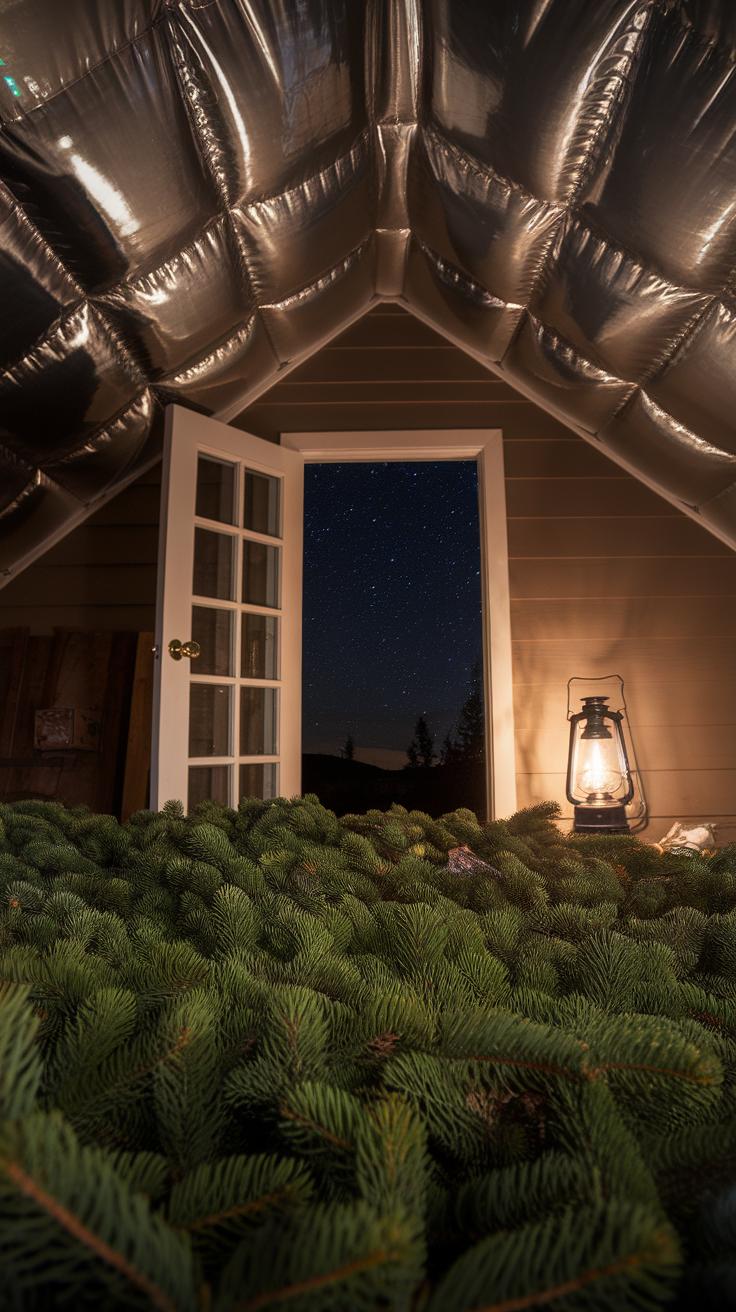

Enhancing Shelter Design for Comfort
When constructing a bushcraft shelter, think about the comfort inside. Insulation plays a key role in regulating temperature. Use materials like leaves, moss, or pine needles to create layers that trap warmth. The thicker the insulation, the cozier the shelter feels during cold nights. Remember, proper ventilation helps maintain fresh air and prevents moisture buildup. Create openings that allow airflow while keeping rain and wind out. This balance prevents dampness, which can lead to discomfort and health issues.
Organization for Functional Living Space
Organizing your shelter makes a significant difference in comfort. Create designated areas for sleeping, cooking, and storage. Use branches or logs to build shelves and keep gear off the ground. This practice not only maximizes space but also helps keep your environment tidy. A clean space promotes better mental well-being, making your bushcraft experience more enjoyable. Keep essential items within easy reach to save time and energy. Following these strategies ensures your shelter remains a comfortable refuge in the wilderness.
Bushcraft Shelter Safety Address safety considerations when living in a bushcraft shelter including fire safety and wildlife precautions

Fire Safety in Bushcraft Shelters
Fire plays a crucial role in bushcraft. It provides warmth, light, and a means for cooking. Always keep safety in mind when using fire. Build your fire pit in a clear area, away from your shelter and flammable materials. Use stones to contain the fire and prevent it from spreading. Make sure to have a bucket of water or dirt nearby to extinguish the fire quickly if needed. When the fire is no longer necessary, completely extinguish it to prevent any possible wildfires. Be aware of fire restrictions in your region, as some areas may prohibit open flames due to dry conditions.
Wildlife Precautions
Living in the wilderness often means sharing it with wildlife. Protect yourself and your food by following simple precautions. Store food and cooking gear away from your shelter. Use a bear bag or a bear canister to hang food from a tree, keeping it out of reach of curious animals. Avoid leaving food scraps around your shelter, as they can attract unwanted visitors. Always be aware of your surroundings. If you encounter wildlife, observe from a distance and do not approach them. Respecting wildlife ensures both your safety and the safety of the animals.
Advanced Shelter Designs for Outdoor Comfort
Creative Techniques for Seasoned Bushcrafters
Experienced bushcrafters can elevate their skills by using advanced shelter designs. One effective method is the A-frame shelter, which provides excellent stability and wind resistance. You can create this structure with two long poles and a covering made of natural materials like leaves or bark. This design allows for proper drainage, keeping you dry in rainy conditions.
Another option is the debris hut, which utilizes surrounding materials to create insulation. Start by constructing a sturdy frame from branches, then pile leaves, pine needles, or grass on top. This approach not only helps you stay warm but also blends into the environment, minimizing visibility.
Consider adding a fire reflector to your shelter site. Building a wall from stones can direct heat towards your sleeping area, increasing warmth during cold nights. Such thoughtful details turn each outing into a more comfortable experience and enhance your bushcraft skills significantly.
Conclusions
Mastering bushcraft shelter design involves understanding the environment, selecting appropriate materials, and applying various construction techniques. This knowledge equips you to create shelters that suit different climates and terrains. From simple lean-tos to more complex structures, your options are numerous and customizable based on your specific needs.
As you venture into the wilderness, remember that the skills you gain in building a smart bushcraft shelter will enhance your outdoor experiences. A well-constructed shelter can provide warmth, safety, and comfort, ultimately making your time in nature more enjoyable. With practice and creativity, you can make each outdoor adventure a memorable one.











